Content
These revenues will be balanced on the assets side, appearing as cash, investments, inventory, or other assets. These questions are looked at through a series of case studies, mostly written by those who are responsible for the balance sheet structures they are living with.
The balance sheet format is fairly simple once you get a hang of it, so don’t be intimidated by the lengthy balance sheet. Simply follow the steps given above and get right into it and don’t fret too much. It is balanced through the financial obligations, equity and earnings. As a company operates, it will steadily keep on balancing this amount. The initial trial balance created in the step one is arranged in the format of the account structure. The entries of the trial balance are to be adjusted to match the records as standardized by the auditors.
Types
Net income is the accountant’s term for the amount of profit that is reported for a particular time period. The amount of retained earnings is the difference between the amounts earned by the company in the past and the dividends that have been distributed to the owners. The balance sheet format has been designed https://www.bookstime.com/ to create a statement of finance that is standardized across companies. Balance sheet format as per schedule 6 requires liabilities and assets to be classified in terms of current and non-current. The consolidated balance sheet format is slightly tricky compared to the usual balance sheet format.
- Secondly, to enable shareholders and investors to evaluate the firm’s recent financial performance and prospects for future growth.
- Items of value the firm owns or controls, which it uses to earn revenues.
- The first part of a cash flow statement analyzes a company’s cash flow from net income or losses.
- The B/S, therefore, differs from other statements, which report activity for a specific period.
- Those familiar with accounting systems may also note that most of the Balance sheet line items are also the names of accounts from the firm’s Chart of Account.
In an unclassified balance sheet, all assets are shown without making any classification. Similarly, liabilities are also shown without making any classification. Inventory cost is based on specific identification or estimated using the first-in, first-out or weighted average cost methods. Some accounting standards also allow last-in, first-out as an additional inventory valuation method.
Farm Management Newsletter
Strong branding ultimately pays off in customer loyalty, competitive edge, and bankable brand equity. Take control of asset TCO and prevent nasty cost surprises later. Businesspeople seeking funding for projects, acquisitions, or investments start with the hurdles event. Measure and prove the value of every benefit—financial, nonfinancial, or “intangible.”
According to the historical cost principle, all assets, with the exception of some intangible assets, are reported on the balance sheet at their purchase price. In other words, they are listed on the report for the same amount of money the company paid for them. This typically creates a discrepancy between what is listed on the report and the true fair market value of the resources. For instance, a building that was purchased in 1975 for $20,000 could be worth $1,000,000 today, but it will only be listed for $20,000.
Fixed or long-term assets
Information and suggestions regarding business risk management and safeguards do not necessarily represent Wells Fargo’s business practices or experience. Please contact your own legal, tax, or financial advisors regarding your specific business needs before taking any action based upon this information. Current balance sheet assets are cash and those items that are likely to become cash in one year or less, such as inventory, accounts receivable , and notes receivable . Assets include the value of everything owned by and owed to the business. On a balance sheet, assets are usually split into current and non-current assets.
- Any increase in one will inevitably be accompanied by an increase in the other, and the only way to increase the owners’ equity is to increase the net assets.
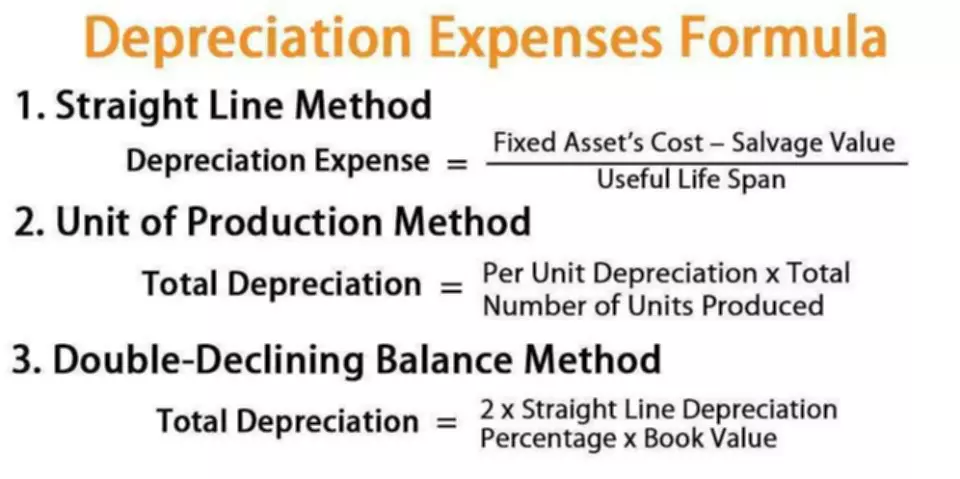
- For example, a positive change in plant, property, and equipment is equal to capital expenditure minus depreciation expense.
- Strong branding ultimately pays off in customer loyalty, competitive edge, and bankable brand equity.
- The Balance Sheet (B/S) is one of 4 primary financial statements that public companies must publish after every quarter and year.
- Examples of tangible assets include land, buildings, equipment, machinery, furniture, and natural resources such as mineral and petroleum resources.
However, their claims are discharged before the shares of common stockholders at the time of liquidation. ShareholdersA shareholder is an individual or an institution that owns one or more shares of stock in a public or a private corporation and, therefore, are the legal owners of the company. The ownership percentage depends on the number of shares they hold against the company’s total shares. Current Assets is an account on a balance sheet that represents the value of all assets that could be converted into cash within one year. The image below is an example of a comparative balance sheet of Apple, Inc.
Notes
First and foremost, there is a slight modification in the assets section. The accurate market value needs to be taken into consideration for the assets of the subsidiaries. Overall, liabilities will represent loss, or any expenses going outward from the organization. The current liabilities are short term liabilities that are supposed to be taken care of within the year.

Larger businesses tend to have more complex balance sheets, and these are presented in the organization’s annual report. Large businesses also may prepare balance sheets for segments of their businesses.